Stable and Robust Degrading Enrichment Culture for 1,4-Dioxane Bioremediation
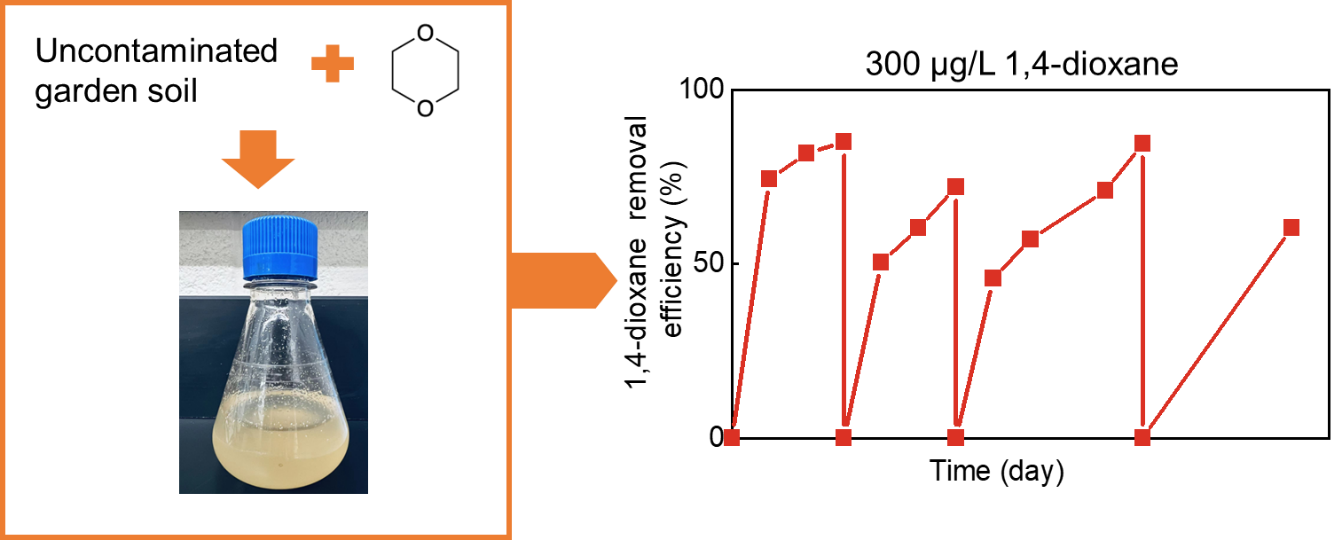
1,4-Dioxane is a contaminant of emerging concern that has been commonly detected in groundwater. In a recent study by researchers at the Center for Clean Water Technology, a stable and robust 1,4-dioxane degrading enrichment culture was obtained from uncontaminated soil. The enrichment was capable of metabolically degrading 1,4-dioxane at both high and environmentally relevant concentrations. The enrichment culture can adapt to both acidic and alkaline conditions and can recover degradation from low temperature and anoxic conditions. The results demonstrated indigenous stable and robust 1,4-dioxane degrading enrichment culture can be obtained from uncontaminated sources and can be a potential candidate for 1,4-dioxane bioaugmentation at environmentally relevant conditions. Findings have been published in Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology; full article available here.